A video is composed of a sequence of images in rapid succession such that the objects, as you browse through the images, appear to be moving. Thus, image processing can be done on these images by looping through them and applying the same algorithm to each image.
In commercial cameras, they describe the rate at which a video is captured by fps or "frames per seconds". The most common cameras has 30fps. For this activity, the fps of a Canon 550D is 50. Since the time interval is just the inverse of the frame rate, the time interval between successive images is 0.02 seconds.
The goal of the activity is to observe the spread of a red
dye in water – hot, cold, and tap. The dispersion of the red in water is
tracked using color segmentation.
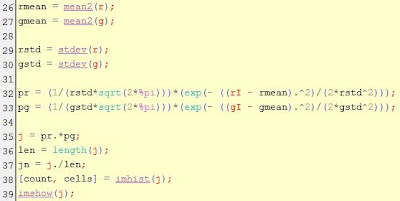
From the last activity, the most effective method
for color segmentation is the non-parametric probability distribution estimation. This
is done by getting the histogram of a region of interest. The color we perceive usually varies due to the uneven level of brightness in an object ,thus, the color space used is the NCC (normalized
chromaticity coordinates) which separates the chromaticity and color
information. The histogram of the ROI (region of interest)
represents a blob in the NCC diagram. Through histogram back projection, each
pixel location in the image has a corresponding value equal to the histogram
value in the chromaticity space. These new set of values make up the image which
should show part of the original image that has the same chromaticity as the
region of interest.
The figure below shows the area of the red dye when it first
touched the water.
 |
| Area of the the red dye as it touched the water |
The red dye was allowed to spread for 30 seconds. The video was parsed into images using
Avidemux with a total of 75 images for processing.
For each image, color segmentation through non-parametric probability
distribution was done. The algorithm was looped through each image.
 |
| Histogram and result of segmentation |
 |
| Plot of the area versus the image number |
It can be observed that after 30 seconds, the red dye was
observed to spread significantly. In order to quantify its dispersion for the 3
set-ups, the mean and the standard deviation of the area for all the images were computed. The table below shows the mean and standard deviation for the hot,
cold and tap water setup.
 |
| Mean and Standard Deviation of the Area of Dispersion of the Red Dye |
Among the 3 setups, the red dye spread most widely in the
hot water setup. This is due to the fact that water molecules in hot water move
faster than in cold water, thus, making the dye spread faster in the medium.
I give myself a 10 for accomplishing the tasks required in
this activity. J
References:
1.
Soriano, M., Activity 11 – Color Segmentation.
2.
Soriano, M., Basic Video Processing